Our daily lives depend greatly on plentiful global resources. MC believes it is important to simultaneously generate three kinds of value: economic value, societal value, and environmental value - while benefiting in a sustainable manner from limited resources within our planetary boundaries. MC’s Environmental Charter positions this as a key consideration in business activities by clarifying that we will promote the sustainable use of natural resources including energy, minerals, food stocks, wood and water throughout our global business operations. Specifically, MC strives to recycle, reuse, and efficiently use resources, reduce the ecological footprint of our business activities, maintain healthy stocks in fishing activities, and otherwise efficiently utilize resources in accordance with our business operations.
| Officer in Charge | Kenji Kobayashi (Senior Vice President, Corporate Functional Officer, CSEO) |
|---|---|
| Deliberative Body (A subcommittee under the Executive Committee, a management decisionmaking body) |
Sustainability Committee Important matters related to the efficient use of resources deliberated in the Sustainability Committee are formally approved by the Executive Committee and put forward or reported to the Board of Directors based on prescribed standards. |
| Department in Charge | Sustainability Dept. |
When reviewing and making decisions on loan and investment proposals, MC conducts a comprehensive screening process which considers not only economic aspects, but ESG factors as well. This includes considering measures to address recycling and closed-loop businesses, waste management and related matters. Besides screening new investment and exit proposals, MC also strives to make improvements to existing business investments by monitoring their management practices.
With regard to waste emissions in its Head Offices, in principle, MC aims to reduce emissions by 1% from the previous fiscal year, and targets are set based on the previous fiscal year’s results. In addition, with regard to recycling rates, MC has set a goal of achieving zero waste emissions offices*MC defines “zero emissions” as cases where vendors are contracted to recycle 95% or more of waste produced by its Head Offices. MC also promotes waste reduction, reuse, and recycling, and manages Head Office activities with waste emissions targets.*, with the aim of recycling at least 95% of the waste produced by MC.
| FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waste | Emissions volume | 431 | 485 | 898*1Includes waste from office renovation*1 |
| • Recycling volume | 425 | 467 | 888 | |
| • Waste volume | 6 | 18 | 11 | |
| Recycling rate (%) | 99% | 96% | 99% | |
Scope of aggregation (Non-Consolidated): Head Office and certain other offices in Tokyo
Nosan Corporation, a consolidated subsidiary of MC, uses Eco Feed*A livestock feed manufactured using by-products of food production (by-products obtained from the food production process), unsold food products (bread and boxed lunches, etc.) leftovers from cooking (cut vegetable scraps and other leftovers from cooking) and residual farm products (imperfect farm produce, etc.).* as a raw material for its formulated livestock feed, with the aim of helping to increase the food recycling rate and enhance the livestock feed and food self-sufficiency rate. Currently, Nosan Corporation uses approximately 7,000Mt per year of dried Eco Feed recycled from discarded by-products of food production, unsold food products, leftovers from cooking etc., as well as approximately 20,000Mt per year of by-products from bakeries and confectionery factories (breadcrumbs, cake flour). These are used as raw materials for livestock feed.

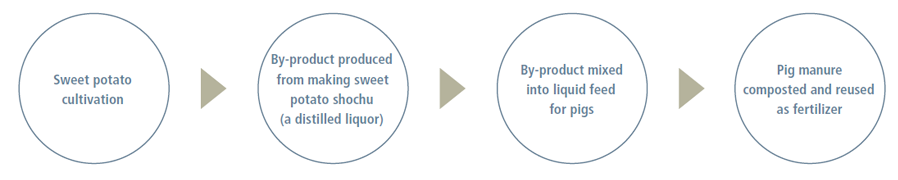
Japan Farm Holdings Inc., a consolidated subsidiary of MC, is a large-scale livestock company that is working to build a closed-loop recycling model. The model is centered on reusing waste generated from a primary industry, specifically the lees left over from producing the distilled liquor shochu. Japan Farm Holdings is located in Kagoshima Prefecture, which is famous for sweet potato shochu manufacturing. The by-product waste known as lees from shochu manufacturing had been an ongoing issue. To solve this problem, Japan Farm worked in collaboration with local distilleries for over two years to develop feed that reuses the shochu lees. The feed is used for breeding pigs for “Brand Pork.” In addition to reducing waste disposal costs and CO2 emissions, this model also involves the manufacture of fertilizer from manure produced by the pigs that consume the feed. This fertilizer is then sold by local vendors, such as agricultural cooperatives, for use in farming.
Japan Farm also maintains and operates a biomass power generation facility that uses chicken manure from the farm as fuel to generate "steam and electrical energy" for effective use. The electricity generated is used as a power source for the facility, while the steam generated by the boiler is used as a heat source. Ash generated during the incineration process is sold to outside parties as a raw material for fertilizers that contains effective minerals.
In January 2020, MC entered the PET chemical recycling business (MC’s equity share: 34%) through an investment in Thai Shinkong Industry Corporation Ltd., which produces PET resins for beverage bottles.
PET is highly recyclable mono-material with a wide range of applications, including in food and beverage containers as well as in textiles, thanks to its excellent transparency, barrier properties, and well-established collection and recycling systems. As the transition to a circular economy progresses worldwide, we will expand our capacity for producing PET resins, for which demand is expected to grow in line with the shift towards mono-materials, and by introduce chemical recycling technologies*2A recycling method in which used plastics are chemically decomposed into the raw material (molecular level) and then re-polymerized. This allows reuse of resources without any degradation in quality due to recycling.*2 through our participation in the PET chemical recycling business with the aim of “Conserving and Effectively Utilizing Natural Capital”.
While environmental awareness in relation to plastics is heightening worldwide, plastics are highly functional basic materials that underpin sustainable economic development. In promoting its plastics business, MC aims to contribute to building a circular society by improving recycling rates and developing alternative materials.
